Verzending 24–48 u • Levering in de hele EU • Veilige chemieverpakking
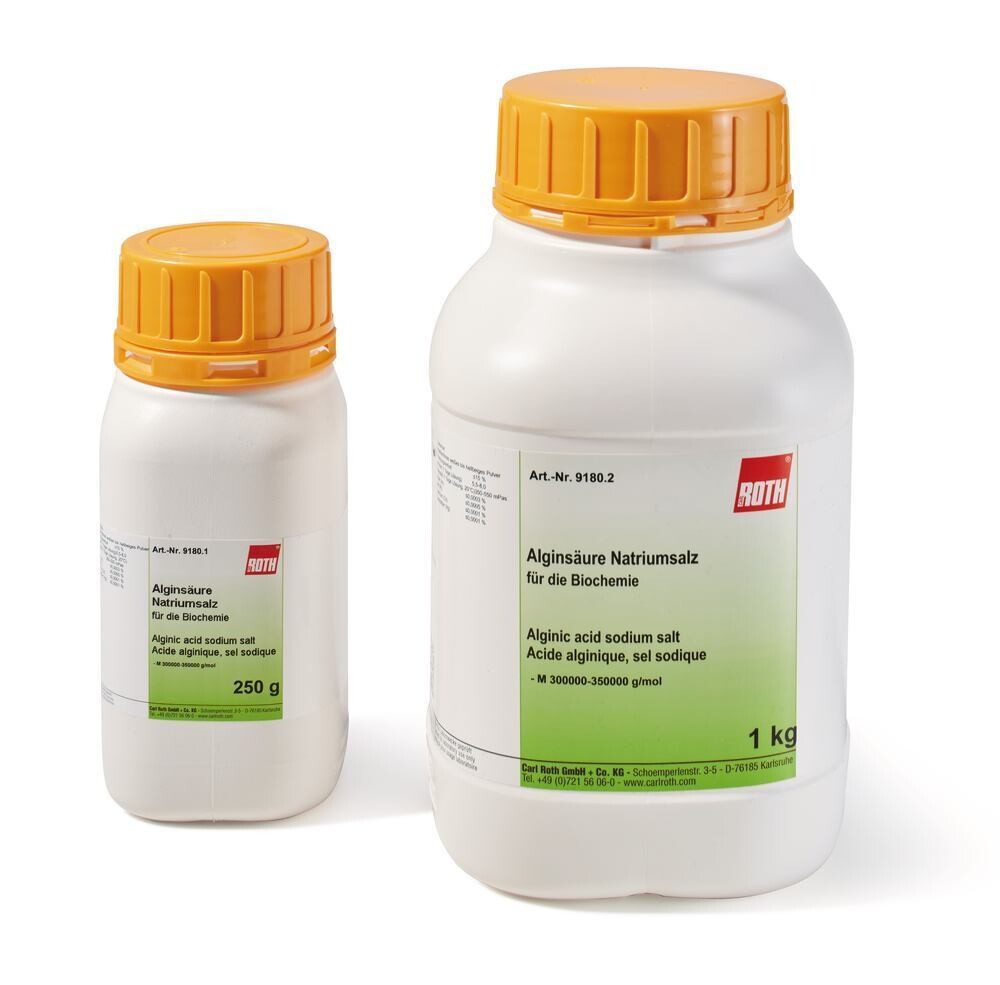
Alginic acid sodium salt, 250 g
SKU 9180.1
€ 52,80
In stock
1
Save this product for later
Alginic acid sodium salt, 250 g
Product Details
P-phrases: P260 P280 P303+P361+P353 P304+P340 P305+P351+P338 P308+P311
H-phrases: H301+H311+H331-H314-H317-H335-H341-H350-H370
CAS number: 50-00-0
Chemical formulas: CH2O
Hazard class: 8 III
HS code: 39131000
Brand: Carl Roth
Alginic acid sodium salt, for biochemistry, Molar mass (M) 300000-350000 g/mol, CAS No. [9005-38-3]
Sugar (Carbohydrates)
Carbohydrates or Saccharides make up 50 % of the dry biomass of the earth and are therefore the most frequent class of biomolecules. Besides at least two hydroxy groups, they also have an aldehyde or a ketone group and can be subdivided according to the number of monomeric components in mono-, di-, oligo and polysaccharides.
Whereas mono-, di- and oligosaccharides are soluble in water, taste sweet and are therefore called as sugar, polysaccharides are hardly, or not at all, soluble in water and have a neutral taste.
Carbohydrates, together with fats and proteins make up a large percentage of nutrition. In addition to their central role as an energy source, they are also an important structural component especially in plants (e.g. Cellulose). Ribose, a monosaccaride with five carbons (C5H10O5) is an essential element of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD and NAD) and a structural component of RNA. Desoxyribose (a ribose derivative) is a structural component of DNA.
Oligo- and polysaccharides
Oligosaccharides consist of three to nine monosaccharide units.
Polysaccharides are macromolecular substances that consist of ≥10 monosaccharide units. A distinction is made between homoglycans, which are made up of only one type of monosaccharides (e.g. starch) and heteroglycans, which consist of at least two different monomeric components (e.g. xanthan).
| Appearance | white to light beige powder |
| Loss on drying | ≤15 % |
| pH-value (1 % solution) | 5,5-8,0 |
| Viscosity (1 % solution, 20 °C) | 350-550 mPas |
| Arsenic (As) | ≤0,0003 % |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤0,0005 % |
| Cadmium (Cd) | ≤0,0001 % |
| Mercury (Hg) | ≤0,0001 % |
You May Also Like
End user declaration required

Acetone 99.9 +% Pure 5 Liter
Acetone 99.9 +% Pure 5 Liter
Only for registered companies
SKU AC045.2
€ 34,79
End user declaration required

Benzoyl chloride 99.9+% Ultra pure 500 Milliliter
Benzoyl chloride 99.9+% Ultra pure 500 Milliliter
Only for registered companies
SKU BZG34.2
€ 24,10
End user declaration required

Chloroform 99,98% p.a. 500 Milliliter
Chloroform 99,98% p.a. 500 Milliliter
Only for registered companies
SKU CHL34.2
€ 13,86
Display prices in:EUR