Verzending 24–48 u • Levering in de hele EU • Veilige chemieverpakking
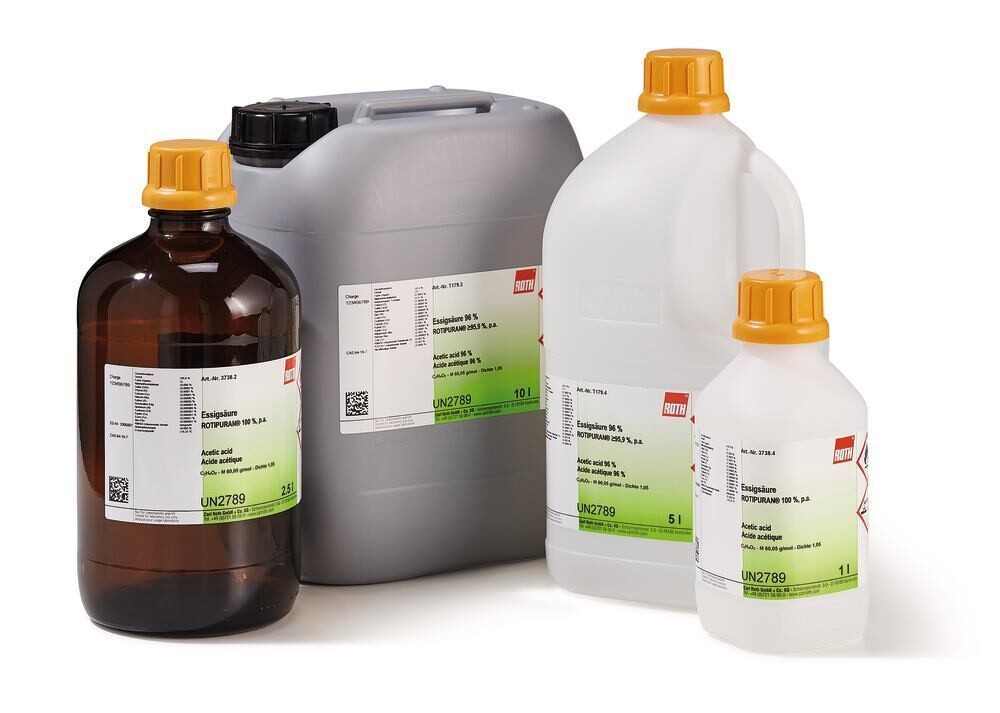
Acetic acid, 5 l, plastic
SKU 3738.6
€ 140,92
In stock
1
Save this product for later
Acetic acid, 5 l, plastic
Product Details
CAS number: 56-40-6
Chemical formulas: C2H5NO2
HS code: 29152100
Brand: Carl Roth
Acetic acid 100 %, ROTIPURAN®, p.a., Molar mass (M) 60,05 g/mol, Density (D) 1,04 g/cm³, Flash point (flp) 39 °C, Boiling point (bp) 117,9 °C, CAS No. [64-19-7], UN-Nr. 2789, EG-Nr. 200-580-7, Empirical formula C2H4O2
Iodine Value Determination
The iodine value is a measure of the unsaturated fatty acids in glycerides. The more olefinic double bonds there are in the fat, the higher the iodine value.
Peroxide Value Determination
The peroxide value of a substance denotes how much peroxide it contains. In a mixture of glacial acetic acid and chloroform, the peroxide oxidises the iodide into elementary iodine. The resulting quantity of iodine is then back-titrated using a thiosulphate solution (where a starch solution is used as the indicator). The blank solution tested in parallel is used to calculate the results.
Barfoed’s test:
Barfoed’s test is used to distinguish monosaccharides from disaccharides, oligosaccharides and polysaccharides. Barfoed’s reagent is added to the sugar solution, which is then heated for a few minutes in a water bath. Monosaccharides turn a reddish colour, while disaccharides only react after they have been boiled for a longer period.
Acids and Bases for Analysis (p.a.)
Carl ROTH provides suitable acids and bases for different requirements!
- High purity
- High batch consistency
- Detailed specifications
- Good price-performance ratio
ROTI®Calipure standards for your calibration needs
Carl ROTH offers an extensive range of calibration and control standards. These products are manufactured from highly pure starting material and are specially tested for each application. The corresponding batch-specific certificate of analysis is available online. Each product series offers excellent value for money.
| Assay | ≥99.8 % |
| Colour (Hazen) | ≤5 |
| Aldehydes/acetaldehyde | ≤0.005 % |
| Sulphate (SO4) | ≤0.0002 % |
| Chloride (Cl) | ≤0.0001 % |
| Calcium (Ca) | ≤0.00001 % |
| Sodium (Na) | ≤0.00005 % |
| Potassium (K) | ≤0.00005 % |
| Mercury (Hg) | ≤0.000001 % |
| Aluminium (Al) | ≤0.000005 % |
| Cadmium (Cd) | ≤0.000001 % |
| Copper (Cu) | ≤0.000001 % |
| Iron (Fe) | ≤0.00001 % |
| Lead (Pb) | ≤0.000001 % |
| KMnO4 reducing substances | complies |
| Evaporation residue | ≤0.003 % |
| Solidification point | ≥16.35 °C |
| Note: Product may crystallise. It can be liquefied by heating in a water bath to max. 40 °C. | |
You May Also Like
End user declaration required

Barium Nitrate 99.8 +% Extra pure 2.5 Kilogram
Barium Nitrate 99.8 +% Extra pure 2.5 Kilogram
Only for registered companies
SKU BANO3983.4
€ 51,35
End user declaration required

Sodium chlorite 25% 20 Liter
Sodium chlorite 25% 20 Liter
Only for registered companies
SKU NCL91.1.3
€ 157,40
End user declaration required

Sodium Borohydride 98 +%, pure 50 gram
Sodium Borohydride 98 +%, pure 50 gram
Only for registered companies
SKU NHH932.2
€ 33,50
Display prices in:EUR