Verzending 24–48 u • Levering in de hele EU • Veilige chemieverpakking
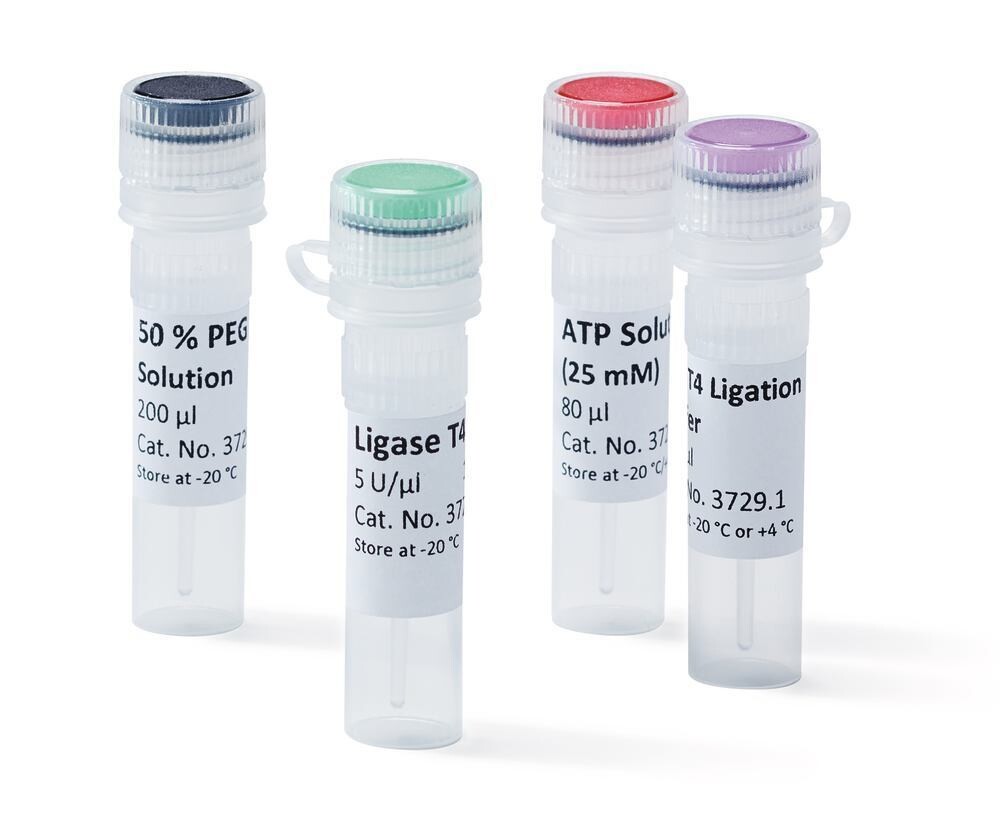
Ligase T4, 100 µl, 1x 500 U
SKU 3729.1
€ 140,92
In stock
1
Save this product for later
Ligase T4, 100 µl, 1x 500 U
Product Details
HS code: 35079090
Brand: Carl Roth
Ligase T4, 5 U/µl, for Molecular Biology, Density (D) 1,18 g/cm³, Storage temp. -20 °C
Ligase T4 5 U/µl, for molecular biology
ATP-dependent recombinant ligase for molecular cloning, site-directed mutagenesis, pitch repair in duplex DNA, RNA or DNA/RNA hybrids and ligation-mediated PCR.
- Cloning of PCR and restriction fragments
- Self-circulation of linear DNA
- Site-directed mutagenesis
T4 DNA Ligase catalyses the formation of a phosphodiester bond between adjacent 5'-phosphate and 3'-hydroxyl end groups in duplex DNA or RNA.
The kit contains:
T4 DNA Ligase
Ligation buffer (10x)
ATP solution (25 mM)
The individual components of this kit cannot be purchased separately.The tubes included in the kit are colour coded to avoid confusion of reagents.
Enzyme: a neoclassical, Greek artificial word ενζυμου, énzymon, derived from εν-, en- (in-) and ζυμη, zýmé (yeast, sourdough, archaic)
Ferments: comes from the Latin fermentum (ferments, sourdough)
There are six classes in which all enzymes are classified according to the particular reaction they catalyse:
• Oxidoreductases (catalyse redox reactions)
• Transferases (transfer functional groups among substrates)
• Hydrolases (cleave bonds via addition of water)
• Lyases/Synthases (cleave or synthesise complex products out of basic substrates without cleavage of ATP)
• Isomerases (transform chemical isomers)
• Ligases/Synthetases (cleave or synthesise complex products out of basic substrates via cleavage of ATP)
| Concentration | 5 U/µl |
| DNA nucleases | not detectable |
You May Also Like
Display prices in:EUR

![N-[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-2-YL-[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-4-AMINE, 98.0%, 250mg N-[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-2-YL-[1,1'-BIPHENYL]-4-AMINE, 98.0%, 250mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4780576667.png)

![TERT-BUTYL 4-(2-OXO-2,3-DIHYDRO-1H-IMIDAZO[4,5-B]PYRIDIN-1-YL)PIPERIDINE-1-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 1g TERT-BUTYL 4-(2-OXO-2,3-DIHYDRO-1H-IMIDAZO[4,5-B]PYRIDIN-1-YL)PIPERIDINE-1-CARBOXYLATE, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4771499628.png)


![6,7-DIHYDRO-5H-PYRROLO[1,2-B][1,2,4]TRIAZOLE, 95.0%, 100mg 6,7-DIHYDRO-5H-PYRROLO[1,2-B][1,2,4]TRIAZOLE, 95.0%, 100mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4868316667.png)

![5H-Dibenzo[b,f]azepine, 95.0%, 100g 5H-Dibenzo[b,f]azepine, 95.0%, 100g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4863727881.png)


