Verzending 24–48 u • Levering in de hele EU • Veilige chemieverpakking
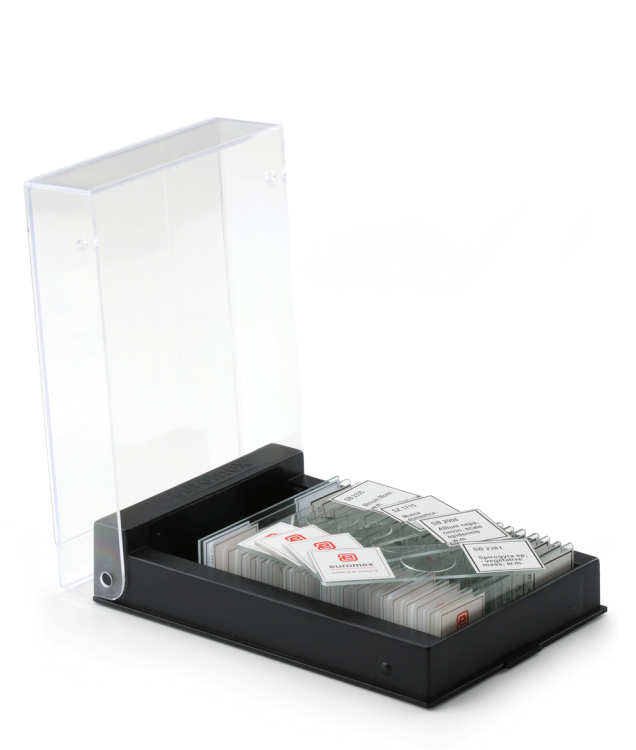
Micro preparation sets (hobby) with 10 preparations
SKU PB.5204
€ 38,00
In stock
1
Save this product for later
Micro preparation sets (hobby) with 10 preparations
Product Details
EAN: 8,95E+12
Brand: Euromex
Type Preparation: set
[tab name='Description']
Set with 10 (PB.5204) micropreparations for hobby: animal and botany. Each set contains a variety of micropreparations. All micro preparations are supplied in a plastic preparation box for 25 preparations.
This set contains:
DOELOGY
SH.1040 Smooth muscle rabbit, cs and ls
SH.1110 Lung rabbit with injected blood vessels cs
SZ.1708 Honeybee, Apis mellifica, mouthparts
SZ.1733 Cabbage White, Pieres brassicae, part of wing
SZ.1877 Frog, Rana spec., blood smear
SB.2015 Buttercup, Ranunculus, root, cs
BOTANCY
SB.2160 Lily, Lilium, leaf, cs
SB.2222 Shepherd's purse, Capsella, Seed box with embryo in cotyledon stage, ls
SB.2374 Nigerfungus.Aspergillus,wm
SB.2384 Ball algae, Volvox sp., wm
––––––––––––––– –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Abbreviations
cs = cross section
ls = longitudinal section
wm = whole specimen
––––––––––––––––––––––– ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
[tab name='Technical Specifications']< /p>
How are cells stained and samples prepared?
Cell staining techniques and preparation depend on the type of staining agent and analysis method. One or more of the following procedures may be necessary to prepare a sample:
• Permeabilization - treatment of cells, usually with a mild surfactant that dissolves cell membranes to allow larger dye molecules to enter the cell
• Fixation - serves to "fix" or maintain cell or tissue morphology through the perparation process. This process can include several steps, but most fixation procedures involve adding a chemical fixative that creates chemical bonds between proteins to increase their strength. Common fixatives include formaldehyde, ethanol, methanol, and/or picric acid
• Mounting - involves attaching samples to a slide for observation and analysis. Cells can be grown directly on the slide or single cells can be applied to a slide using sterile techniques. Thin sections (slices) of material - such as tissue - can also be placed on a microscope slide for observation
• Staining - the application of staining agent to cells, tissues, components, or metabolic processes of cells to color. This method may include immersing the sample (before or after fixing or mounting) in a dye solution and then rinsing and observing the sample under a microscope. Some dyes require the use of an etchant, which chemically reacts with the colorant to produce an insoluble colored result. The etched dye will remain on/in the sample when the excess dye solution is rinsed away
You May Also Like

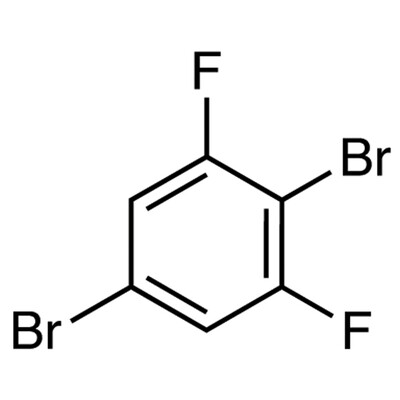
1-(5-Methylfuran-2-yl)propan-1-amine, 95.0%, 1g
1-(5-Methylfuran-2-yl)propan-1-amine, 95.0%, 1g
SKU F244673-1G
€ 1 894,20
Display prices in:EUR






![6-CHLORO-7-METHYL-[1,2,4]TRIAZOLO[4,3-B]PYRIDAZINE, 95.0%, 2g 6-CHLORO-7-METHYL-[1,2,4]TRIAZOLO[4,3-B]PYRIDAZINE, 95.0%, 2g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4868246878.png)