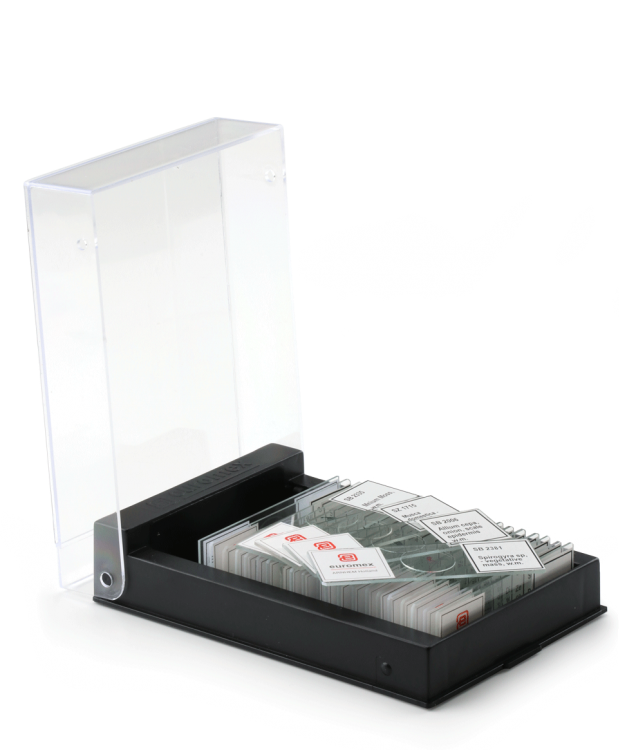
Micro preparation sets (hobby) with 25 preparations
[tab name='Description']
Set with 10 (PB.5204) micropreparations for hobby: animal and botany. Each set contains a variety of micropreparations. All micro preparations are supplied in a plastic preparation box for 25 preparations
This set contains:
HISTOLOGY OF HUMANS AND MAMMALS
SH.1072 Human skin with hair follicle
SH.1150 Human blood smear, Giemsa stain
SH.1415 Motor nerve of rabbit with terminal plate, wm.
SH.1470 Taste buds of rabbit tongue, ls
BOTANICS
SB.2009 Onion, Allium cepa, mitosis root tip ls
SB.2055 Maize, Zea mays, stem, cs
SB.2075 Monocot/dicot stem, maize and pumpkin, cs
SB.2100 Geranium, Pelargonium hortorum, stem, cs
SB.2112 Pumpkin, Cucurbita, stem, cs
SB.2130 Sunflower, Helianthus, leaf, cs
SB.2135 Oleander, Nerium oleander, leaf with sunken stomata, cs< br>SB.2210 Lily, Lilium, anther with developed pollen, cs
SB.2225 Maize, Zea mays, grain with embryo, ls
ZZ.1520 Slipper animals , Paramecium, wm
SZ.1535 Eye animal, Euglena viridis, wm
SZ.1580 Freshwater polyp, Hydra, with budding, wm
SZ.1630 Tapeworm, Taenia of cattle, developed proglottids, wm
SZ .1635 Horse roundworm, Ascaris megalocephala, male and female, cs
SZ.1640 Horse roundworm, Ascaris megalocephala, mitotic eggs
SZ.1655 Water flea, Daphnia sp., wm
SZ.1705 Honey bee, Apis mellifica, hind leg , wm
SZ.1710 Honeybee, Apis mellifica, faceted eye, cs
SZ.1719 Housefly, Musca domestica, wing, wm
SZ.1722 Mosquito, Culex pipiens. mouthparts of female
SZ.1724 Chromosomes, fruit fly, drosophila, salivary gland, wm
–––––––––––––––––––––––– –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Abbreviations
cs = cross section
ls = longitudinal section
wm = entire specimen
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– –––––––––––––––––––––––
[tab name='Technical Specifications']
How are cells stained and samples prepared?
Cell staining techniques and preparation depend on the type of staining agent and analysis method. One or more of the following procedures may be necessary to prepare a sample:
• Permeabilization - treatment of cells, usually with a mild surfactant that dissolves cell membranes to allow larger dye molecules to enter the cell
• Fixation - serves to "fix" or maintain cell or tissue morphology through the perparation process. This process can include several steps, but most fixation procedures involve adding a chemical fixative that creates chemical bonds between proteins to increase their strength. Common fixatives include formaldehyde, ethanol, methanol, and/or picric acid
• Mounting - involves attaching samples to a slide for observation and analysis. Cells can be grown directly on the slide or single cells can be applied to a slide using sterile techniques. Thin sections (slices) of material - such as tissue - can also be placed on a microscope slide for observation
• Staining - the application of staining agent to cells, tissues, components, or metabolic processes of cells to color. This method may include immersing the sample (before or after fixing or mounting) in a dye solution and then rinsing and observing the sample under a microscope. Some dyes require the use of an etchant, which chemically reacts with the colorant to produce an insoluble colored result. The etched dye will remain on/in the sample when the excess dye solution is rinsed away







![[(4-ethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]methylamine dihydrochloride, 95.0%, 5g [(4-ethyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)methyl]methylamine dihydrochloride, 95.0%, 5g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4856274524.png)

![2-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-2-azaspiro[3.4]octane-5-carboxylic acid, 98%, 250mg 2-(tert-Butoxycarbonyl)-2-azaspiro[3.4]octane-5-carboxylic acid, 98%, 250mg](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4857799875.png)

