Verzending 24–48 u • Levering in de hele EU • Veilige chemieverpakking
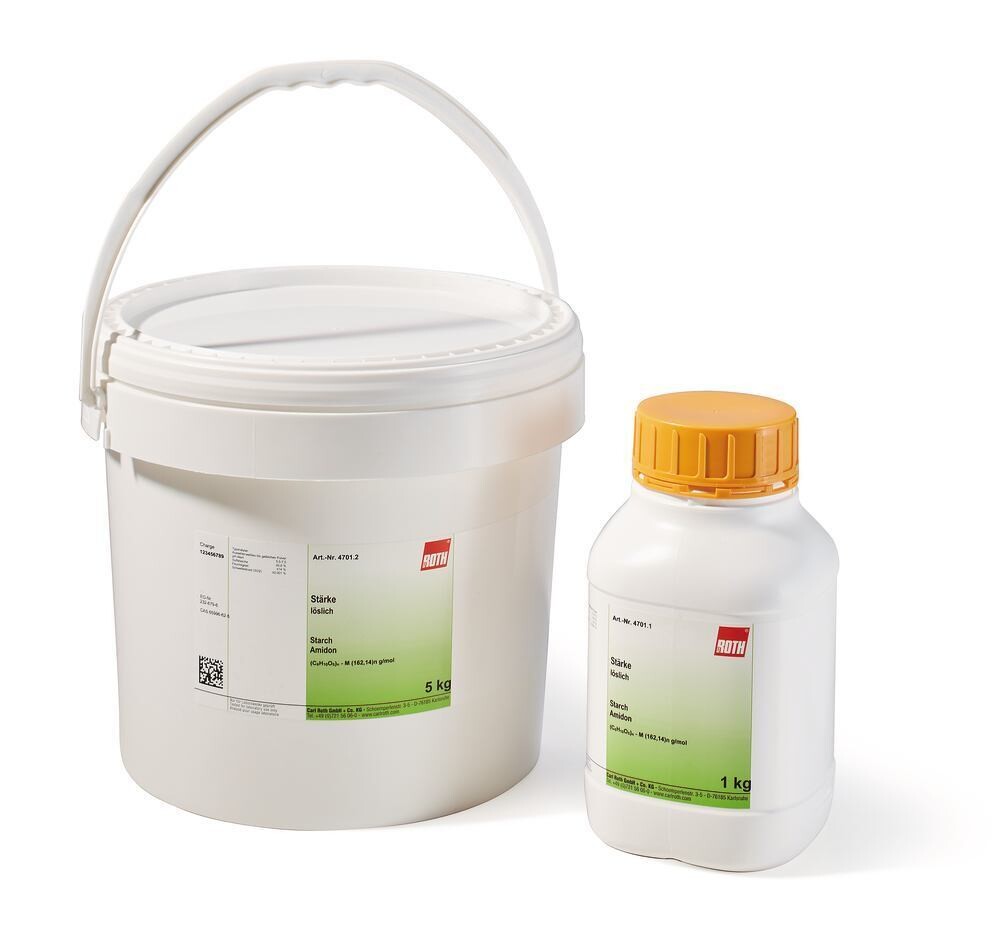
Starch, 5 kg, plastic
SKU 4701.2
€ 116,79
In stock
1
Save this product for later
Starch, 5 kg, plastic
Product Details
HS code: 35051090
Brand: Carl Roth
Starch, soluble, Molar mass (M) (162,14)n g/mol, CAS No. [65996-62-5], EG-Nr. 232-679-6, Empirical formula (C6H10O5)n
Starch soluble
Important compound of many nutrient media for cultivation of fastidious microorganisms in general, and Clostridia in particular. Please solubilise the starch in very few cold water prior to addition to the medium.
Sugar (Carbohydrates)
Carbohydrates or Saccharides make up 50 % of the dry biomass of the earth and are therefore the most frequent class of biomolecules. Besides at least two hydroxy groups, they also have an aldehyde or a ketone group and can be subdivided according to the number of monomeric components in mono-, di-, oligo and polysaccharides.
Whereas mono-, di- and oligosaccharides are soluble in water, taste sweet and are therefore called as sugar, polysaccharides are hardly, or not at all, soluble in water and have a neutral taste.
Carbohydrates, together with fats and proteins make up a large percentage of nutrition. In addition to their central role as an energy source, they are also an important structural component especially in plants (e.g. Cellulose). Ribose, a monosaccaride with five carbons (C5H10O5) is an essential element of coenzymes (such as ATP, FAD and NAD) and a structural component of RNA. Desoxyribose (a ribose derivative) is a structural component of DNA.
Oligo- and polysaccharides
Oligosaccharides consist of three to nine monosaccharide units.
Polysaccharides are macromolecular substances that consist of ≥10 monosaccharide units. A distinction is made between homoglycans, which are made up of only one type of monosaccharides (e.g. starch) and heteroglycans, which consist of at least two different monomeric components (e.g. xanthan).
| Appearance | white to yellowish powder |
| pH-value | 5.5-7.5 |
| Sulphated ash | ≤0.6 % |
| Moisture | ≤14 % |
| Sulphur dioxide (SO2) | ≤0.001 % |
You May Also Like

4-FLUORO-2-DIFLUOROMETHOXYNITROBENZENE, 95.0%, 25g
4-FLUORO-2-DIFLUOROMETHOXYNITROBENZENE, 95.0%, 25g
SKU F306894-25G
€ 2 237,40

3-Chloro-5-methylpyridazine, 97.0%, 100g
3-Chloro-5-methylpyridazine, 97.0%, 100g
SKU F067469-100G
€ 2 935,90

4-Nitrothiophene-2-carbonitrile, 95.0%, 5g
4-Nitrothiophene-2-carbonitrile, 95.0%, 5g
SKU F209150-5G
€ 277,20

Ethyl 2-iso-propylbenzoylformate, 97.0%, 1g
Ethyl 2-iso-propylbenzoylformate, 97.0%, 1g
SKU F201017-1G
€ 336,60
Display prices in:EUR

![N,N,N-trimethyl[1-(triisopropylsilyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]methanaminium iodide, 95.0%, 1g N,N,N-trimethyl[1-(triisopropylsilyl)-1H-indol-3-yl]methanaminium iodide, 95.0%, 1g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4780590992.png)
![Thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-ol, 95.0%, 25g Thieno[3,2-b]pyridin-7-ol, 95.0%, 25g](https://d2j6dbq0eux0bg.cloudfront.net/images/88473019/4771434669.png)